You have probably already heard the name Polygon being thrown around here and there, and perhaps you wondered what Polygon is all about. Most things you hear nowadays are about low transaction fees, NFTs being so much cheaper to mint on Polygon, or MATIC reaching new heights. But it’s time we dig a little deeper and get to know Polygon, the network of sidechains, a little better, so we understand what we are dealing with.
Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum. It is both a framework and a network of sidechains previously known as MATIC network.
What Polygon tries to achieve is to target Ethereum’s current shortcomings (long transaction times, high gas fees) with a network of sidechains. Those sidechains can directly interact with each other but also with Ethereum. Transactions in that sidechain network are way cheaper, take way less time to process, and are regularly synchronized to Ethereum itself.
Framework
The Polygon framework allows you to create a personalized sidechain with a set of customized properties. You get the building blocks you need to create your own chain while maintaining power over how exactly you want to set it all up. The SDK is written in Go and allows a proficient developer to quickly wire together components until you have a working node/client that you can deploy. Everything, especially on a lower level, is taken care of for you. You don’t need to deal with message passing between chains or syncing states; the SDK already has that implemented for you.
Sidechain Network
The sidechain network is where the operational magic happens. Every custom sidechain you build with the SDK is directly interlinked with the Polygon network. The base network offers all scalability functions to operate fast and keep it in sync with Ethereum.
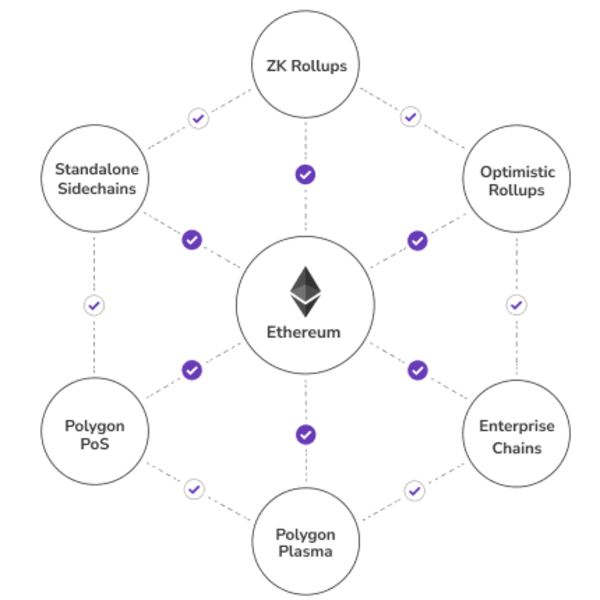
Especially five components of the network are crucial to its operational readiness:
- Polygon PoS
- Polygon Plasma
- ZK Rollups
- Optimistic Rollups
- The Ethereum Layer
Polygon PoS
Polygon PoS adds an overall Proof-of-Stake consensus protocol to Polygon’s network of sidechains.
Polygon Plasma
Plasma is a scaling solution to move assets between the root chain and its child chains through Plasma bridges.
ZK Rollups
ZK Rollups are an alternative scaling solution where many transactions are bundled off-chain into a single transaction. It uses zero-knowledge proofs for the final record on the Ethereum main chain.
Optimistic Rollups
Optimistic Rollups run on top of Ethereum to enable near-instant transactions with the help of so-called fraud-proofs.
The Ethereum Layer
At some point, Polygon needs to interact with Ethereum. This is realized with a set of smart contracts deployed to Ethereum. They enable the communication between Ethereum and all Polygon chains, take care of staking and transaction finality, and the overall communication between the two.
Standalone and Enterprise Chains
Standalone and enterprise chains are the sidechains you implement and deploy with the help of the Polygon SDK. They encourage local communities, governed by their members, developed by the community. Those communities are responsible for consensus on their own, local level, and can interact with all other sidechains and Ethereum to their liking.
Corporations might launch their own sidechain for their projects, keeping control of the direct infrastructure while gaining the opportunity to interact with many other chains. Communities can launch their chains where they develop and deploy their projects on. There are few restrictions on what you can do with your sidechain, making the solution so flexible and worthwhile.
Polygon As A User
Users interacting with Polygon usually only see Polygon as a whole blockchain, and the underlying architecture is not important for the everyday user. Any Ethereum-compatible web wallet can connect to Polygon, acquire funds (MATIC), and interact with dApps deployed somewhere within the network. OpenSea, for example, has allowed minting and trading NFTs on Polygon for a while now. You only need to switch the chain your wallet is connected to, and everything works. The UX is not different from Ethereum, which makes Polygon also an excellent solution usability-wise. Overall, the space might still have a UX problem, but it doesn’t get any worse by choosing Polygon. One could even argue that lower transaction fees and higher processing time improve the UX because who likes waiting for minutes or hours until you finally know whether your NFT mint was successful?
The next time you open Uniswap, go to OpenSea or even want to deploy a smart contract, think about Polygon for a moment. It might be a valid alternative to deploying on Ethereum, at least for now, until Ethereum 2.0 finally hits and hopefully solves many of the original issues. And even after that, Polygon offers a unique approach to scaling and community building with custom sidechains that are fully interoperable with Ethereum.
Before You Leave
Do you like written content like this? If so, you will probably love my newsletter.
Iteration Three is the Web 3 newsletter I would love to get into my inbox each week.
From the latest news in the industry, opportunities, analyses, and development tips, to showcases of interesting new projects, this newsletter tries to give you everything you might have missed or did not even know existed.

